Carbon Steel Pipe
Stainless Steel Pipe
Fittings
OCTG
Steel Structure
Value-Added Products
Clad Pipe
Coated Steel Pipe
Technical Data
Photos
Material of Steel Plate
1. Carbon steel plates
Carbon steel plates are widely used in various fields such as construction, machinery, automotive, shipbuilding, bridges, pressure vessels, household appliances, and mechanical parts due to their excellent mechanical properties, workability, and cost-effectiveness.Carbon steel plates are divided into high carbon steel, medium carbon steel, and low carbon steel. The higher the carbon content, the greater the hardness, strength, and wear resistance of the steel after heat treatment, but also the more brittle it becomes. Conversely, the lower the carbon content, the softer the steel is and the more ductile it becomes.
Common ASTM standards for carbon steel plates include A36, A283, A516, and A570, among others.
2. Mild Steel Plate
To enhance the ductility of carbon steel plates, the carbon content can be reduced to produce low-carbon steel plates with a carbon content of 0.05% to 0.25%. This type of metal is known as mild steel plate. Due to its good workability, it is easy to forge, weld, and cut, making mild steel plates widely used in the manufacture of chains, rivets, bolts, shafts, etc. Additionally, mild steel sheets are also extensively used in building structures, automotive manufacturing, and mechanical parts. Depending on the production process, mild steel plates can be categorized into cold-rolled steel plates and hot-rolled steel plates.To provide additional anti-slip performance and increased strength, mild steel chequered plates are widely used in situations requiring good anti-slip properties, such as working platforms, walkways, stair treads, truck beds, building structures, shipbuilding, and many other industrial and commercial applications. Their thickness typically ranges from 2.5mm to 12mm, and the size can be customized according to specific needs, such as 4 feet by 8 feet or 5 feet by 10 feet. Nansteel also offers galvanized mild steel plates that have undergone zinc plating to meet various demands.
3. Stainless Steel Plate
Stainless steel plates have a smooth surface and possess high plasticity, toughness, and mechanical strength, as well as resistance to corrosion from acids, alkalis, gases, solutions, and other media. The main features include corrosion resistance, good physical properties (heat resistance, high-temperature resistance, low-temperature resistance, and even ultra-low temperature resistance), aesthetic appearance, recyclability, and good hygiene (safe and non-toxic). These characteristics make stainless steel metal plates widely used in industrial fields such as construction, chemical industry, food, pharmaceuticals, papermaking, petroleum, nuclear energy, as well as in consumer goods such as kitchenware, tableware, vehicles, and household appliances. Common materials for stainless steel plates include 303, 304, 316, 316L, 321, 409, 410, 420, etc. Some specific standards for stainless steel plates include ASTM A240, ASTM A263, ASTM A693, and ASTM A264.Production Process of Steel Plates
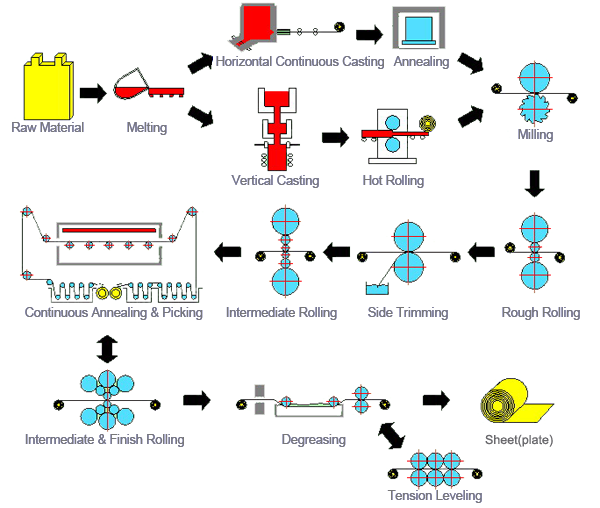
The production process of steel plates, which can be described in the following steps:1.Raw Material: The process begins with the procurement of raw materials, typically iron ore, which is the primary ingredient for steelmaking.
2.Melting: The raw materials are melted in a furnace to produce molten metal, which is a crucial step in converting raw materials into a workable form for further processing.
3.Milling: After melting, the molten metal may undergo milling, a process that refines the metal and prepares it for casting.
4.Vertical Casting: The molten metal is cast into a vertical mold, forming a continuous slab or billet, which is the initial form of the steel plate.
5.Hot Rolling: The cast slab is then hot-rolled, a process that involves passing the slab through rollers to reduce its thickness and achieve the desired dimensions.
6.Continuous Annealing & Picking: The hot-rolled steel is annealed, a heat treatment process that alters its microstructure to improve ductility and reduce hardness. After annealing, the steel is cooled and picked for further processing.
7.Intermediate Rolling: The steel undergoes intermediate rolling, which further refines the thickness and properties of the steel plate.
8.Side Trimming: Excess material from the edges is trimmed off to achieve the desired width of the steel plate.
9.Rough Rolling: The steel plate undergoes rough rolling, which is an initial stage of deformation to reduce the thickness of the slab.
10.Intermediate & Finish Rolling: After rough rolling, the steel plate is subjected to intermediate and finish rolling to achieve the final dimensions and surface quality.
11.Degreasing: The steel plate is degreased to remove any contaminants or lubricants that may be present from previous processes.
12.Sheet(plate): The final product is a sheet or plate of steel, ready for further processing or end-use.
13.Tension Leveling: The steel plate may undergo tension leveling, a process that corrects any residual stresses and ensures a flat surface.
Styles of metal plate
1.Steel tread plate
Tread steel sheets have ridges on their surface, which are non-slip and can be used as floors, factory escalators, work platform pedals, ship decks, car bottom plates, etc. Diamond plate sheets have patterns in lentil-shaped, diamond-shaped, round bean-shaped, and flat-round mixed shapes. The lentil-shaped shape is the most common in the market.
2. Expanded steel sheet
Expanded steel sheet is a kind of metal mesh that expands metal materials to two to ten times the original length.Material: low carbon steel plate, aluminum plate, stainless steel plate, titanium plate
Hole shape: diamond, hexagon, round, special-shaped
Long pitch: 10-150mm, short pitch 5-60mm
Thickness: 0.3-8.0mm
Size: width within two meters, length can be customized according to customer requirements.
Surface: spray anti-rust paint, hot-dip galvanizing, plastic-dipped pipe.
Features: anti-slip, wear-resistant, flat mesh, uniform mesh, high tensile strength, high gravity resistance, light mesh, easy construction, low cost.
3. Perforated steel sheet
Steel plate punching mesh is a metal plate with various hole shapes punched out on the metal plate material. It is usually made of galvanized steel plate, stainless steel plate, copper plate, aluminum plate, nickel plate and alloy plate, and is punched through a punch press through a die. The product has the characteristics of beautiful appearance, strong integrity, uniform mesh, smooth mesh surface, easy processing and low cost.
4. Corrugated steel sheet
Corrugated steel sheet is a type of steel with a corrugated surface, which increases the strength and rigidity of the material while reducing its weight. Corrugated steel is widely used in the construction industry, especially as roof covering material and wall panels, due to its durability, ease of installation and cost-effectiveness. In addition, corrugated steel can also be used in a variety of applications such as temporary structures, containers, noise barriers, etc.
5. Precut steel base plates
Pre-cut steel base plates are steel materials that have been processed to specific dimensions and specifications in advance. They are commonly used as the base or support structure for various industrial and construction projects.| Grade | Thickness | Width | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| A-36 | 3/16" - 8" | 48", 60", 72", 84", 96", 120" | 96", 120", 240", 480" |
| A572GR50 | 3/16" - 5" | 84", 96" | 240" |
| A516GR70 | 3/16" - 1-1/2" | 96" | 240" |
| AR400 | 3/16" - 1" | 48", 60", 96" | 96", 144", 288" |
| Floor Plate | 3/16" - 1" | 48", 60", 72", 96" | 96", 120", 144", 240" |
| 1008/1010 | 1/4" - 1/2" | 48", 60" | 96", 120" |
| Pickled & Oiled | 3/16" - 5/8" | 48", 60", 72" | 96", 120", 144" |











